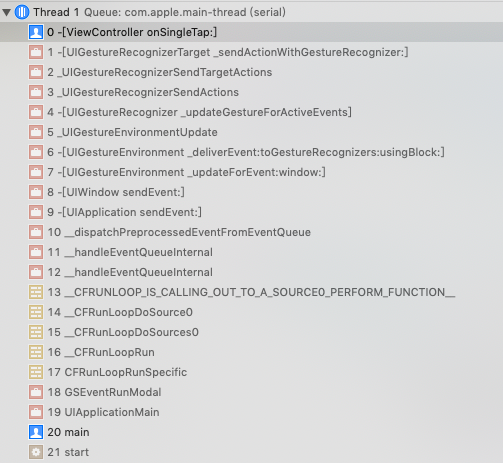
(UIKit Framework) UITouch事件的处理
iOS系统在运行过程中,会收到各种不同的事件,包括touch事件,motion事件,remote control事件以及press 事件。
-
touch事件指的是与设备屏幕间的交互 -
motion事件指的是设备运动相关的事件,例如摇一摇等; -
remote control事件指的是收到外设(例如耳机)发出的命令,例如耳机控制音视频的播放; -
press 事件指的是游戏手柄,apple TV遥控器等有物理按钮的设备间的交互。
我们这里只讨论touch事件与iOS设备屏幕的交互。
当点击屏幕时,iOS系统首先会收到touch事件并分派到相应的app,然后从UIWindow开始自下而上遍历图层,找到最上层touch事件点击的View,即first responder。如果first responder能够处理Touch事件,则触发事件响应的action;否则根据响应链寻找到能够处理 touch事件 的Responder再处理事件。
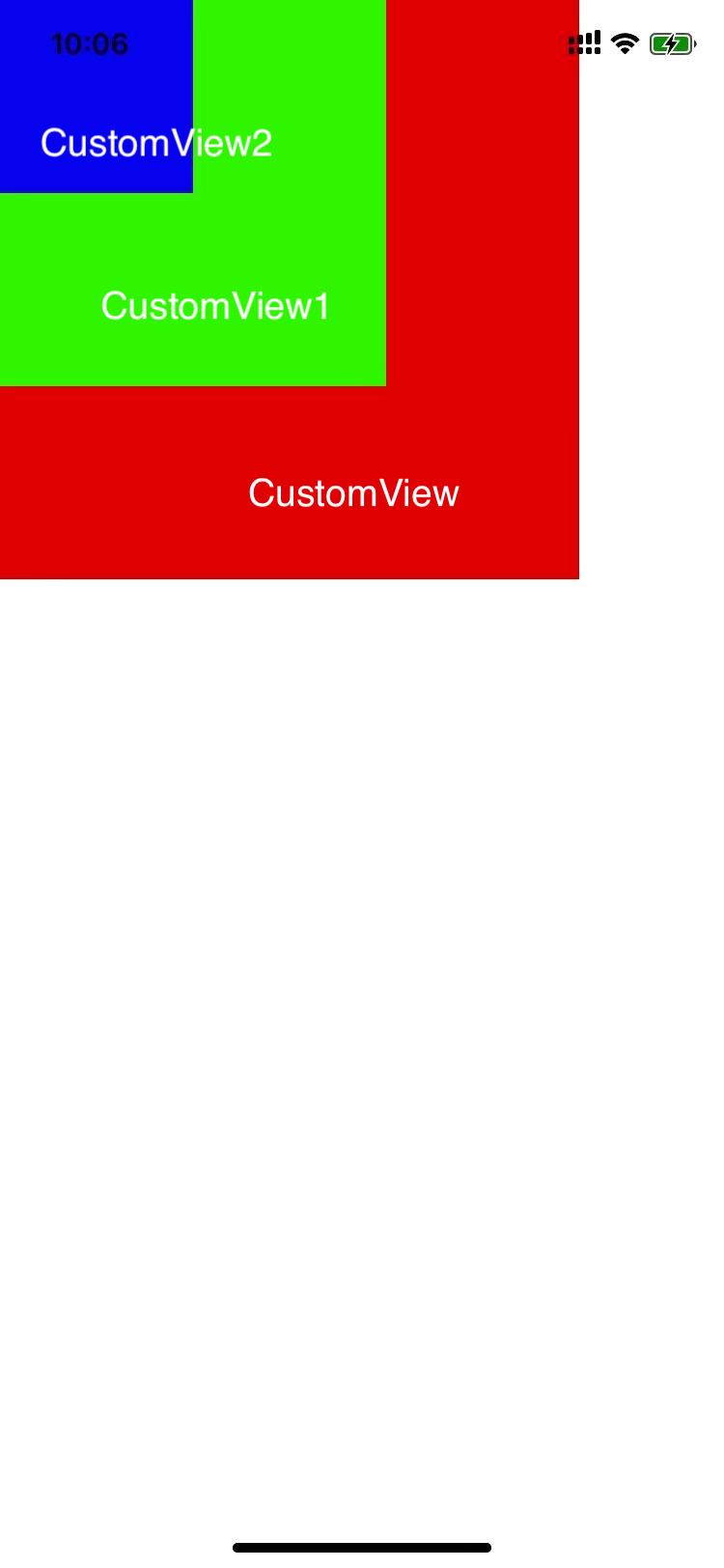
如图所示,有以上的图层关系。
确定first responder
当点击屏幕上CustomView2区域时,首先系统会收到touch事件,然后调用UIWindow的方法 [UIWindow _targetWindowForPathIndex:atPoint:forEvent:windowServerHitTestWindow:] ,该方法会遍历UIWindow的子视图,并调用子视图的 hitTest:withEvent: 确定first responder。
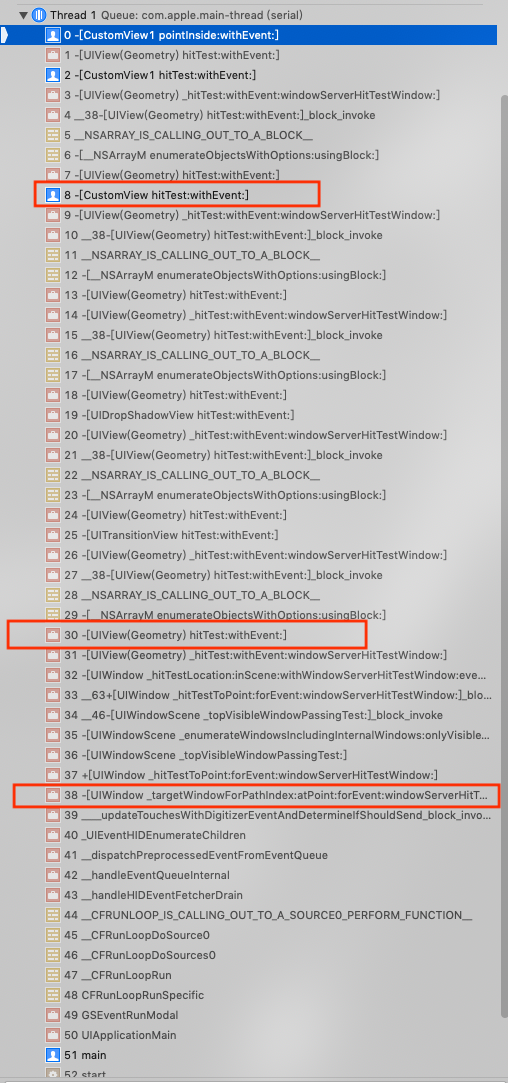
hitTest:withEvent:方法作用是返回touch事件点击的view。如果touch事件没有点击在该view的范围中,则返回nil;如果点击在该view的范围中,则遍历子视图,调用子视图的hitTest:withEvent:方法。具体步骤如下:
-
如果view
hidden设置为YES,alpha设置为0或者userInteractionEnabled设置为NO,则表明view被隐藏或者不处理交互,直接返回nil;否则跳至步骤2 -
如果view没有被隐藏,则调用
pointInside:withEvent:方法,确定touch事件是否点击在view的范围中。如果pointInside:withEvent:返回YES,跳至步骤3;否则返回nil -
遍历子视图,调用子视图的
hitTest:withEvent:,如果子视图返回为nil,则返回自己;如果子视图返回非nil,则返回子视图的结果
根据响应链查找可以处理事件的Responder
当通过hitTest:withEvent:确定了first responder,系统就会调用UIApplication的sendEvent:方法,将事件发送到first responder。
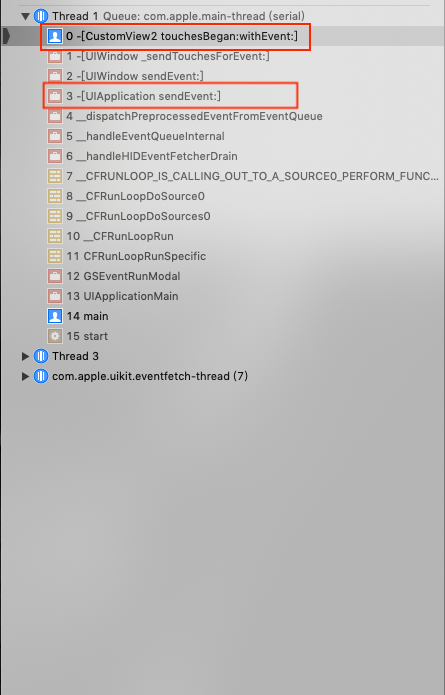
由上图1可以看到CustomView2直接收到了事件,并调用
touchesBegan:withEvent:。
/**
* 通常情况下,任何UIResponder想要自定义的处理touch事件,都要实现以下4个方法。
**/
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event;
- (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event;
如果UIResponder的子类重写了touchesBegan:withEvent:等方法且没有在派生方法中调用父类的touchesBegan:withEvent:方法,则说明该view可以处理该事件,事件就会被拦截不会通过响应链向下传递。
UIControl作为UIResponder的子类,重写了touchesBegan:withEvent:等方法,所以UIButton,UISwitch等收到事件,会直接阻止事件向下传递;而UIView,UIImaeView等则不会阻止事件的传递。
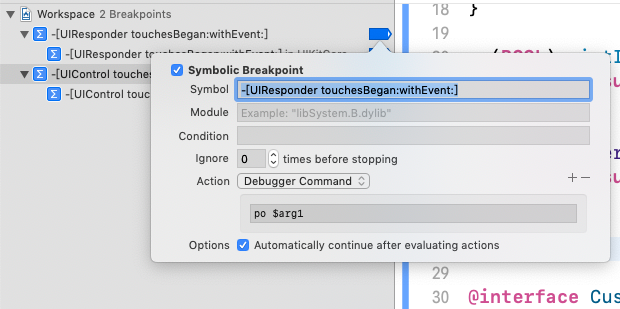
在这里,我们设置了符号断点,追踪了事件的传递。图1所示的
CustomView,CustomView1,CustomView2都直接继承自UIView,且没有重写touchesBegan:withEvent:等方法,所以都不会拦截事件,事件会顺着响应链一直传递到UIApplicationDelegate(这里UIApplicationDelegate是UIResponder的子类)。可以看到事件的传递如下:
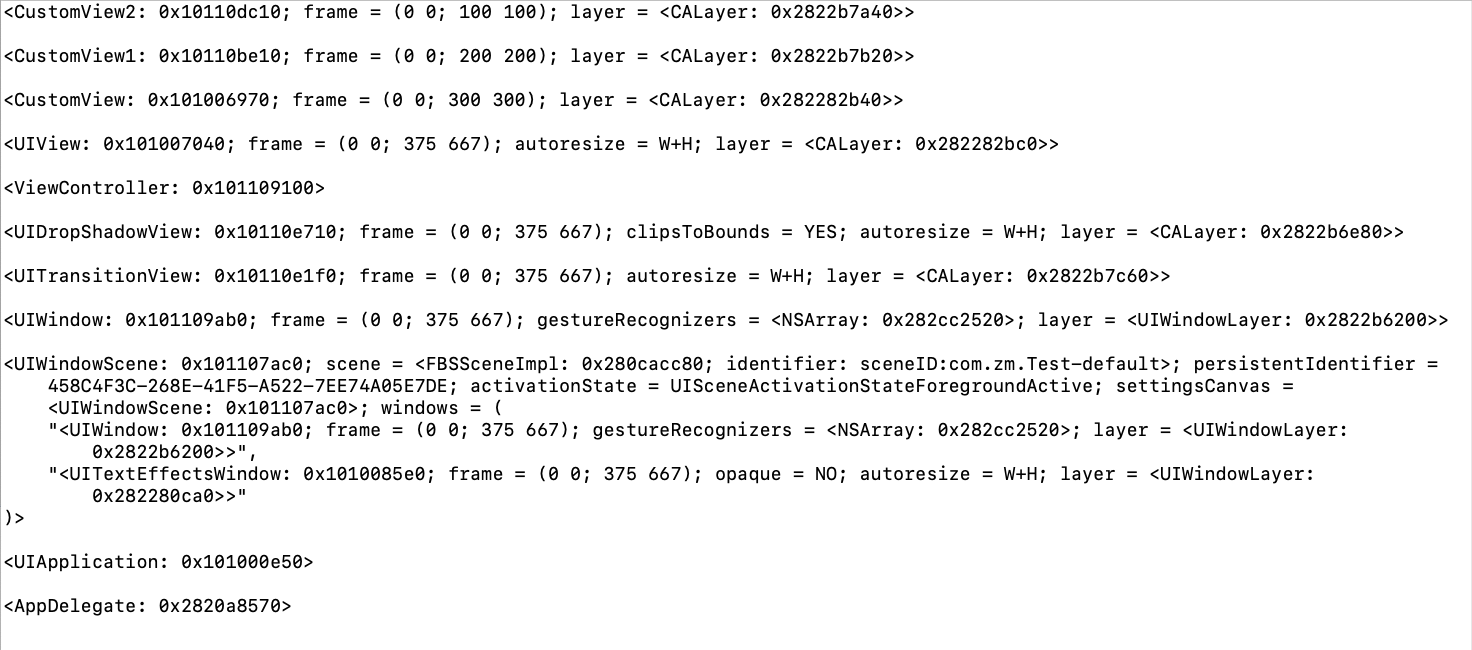
如果将
CustomView1改为继承自UIControl或者重写touchesBegan:withEvent:等方法,则会拦截事件不再传递。可以看到事件的传递如下:

UIControl
UIControl是UIView的子类,是可以响应特定的用户交互视觉元素。Target-Action 机制则是
UIControl 去处理交互的机制。
- (void)addTarget:(nullable id)target action:(SEL)action forControlEvents:(UIControlEvents)controlEvents;
- (void)removeTarget:(nullable id)target action:(nullable SEL)action forControlEvents:(UIControlEvents)controlEvents;
这里我将
CustomView1修改为UIButton,并设置target-action;在点击后,堆栈如下图所示
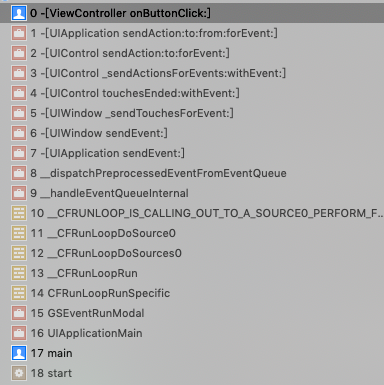
可以看到 UIButton 在 touchesEnded:withEvent: 方法中,
- 根据
UITouch确定了UIControlEvents, 然后确定相应的target和action。 UIControl调用sendAction:to:forEvent方法UIApplication调用sendAction:to:from:forEvent方法- 最终
target调用action方法,即-[ViewController onButtonClick:]
UIGestureRecognizer
touch事件 在响应链中传递时,UIGestureRecognizer 会比它们的 view 先收到 touch事件。如果 UIGestureRecognizer 无法响应 touch事件 ,view 才会收到并处理。